Introduction to Data Engineering
Introduction to Data Engineering
Introduction to Data Engineering
Storage
- AWS S3
- Azure Blob Storage
- Google Cloud Storage
Computation
- AWS EC2
- Azure Virtual Machines
- Google Compute Engine
Databases
- AWS RDS
- Azure SQL Database
- Google Cloud SQL
Data Engineering toolbox
Structured: database schema
- Relational database
Semi-structured
- JSON
Unstructured: schemaless, more like files
- Video, photos
SQL
- Tables
- TB schema
- Relational databases
- MySQL, PostgreSQL
NoSQL
- Non-relational databases
- Structured or unstructured
- Key-value store (e.g caching)
- Document DB(e.g JSON objects)
- Redis, MongoDB
Star Schema
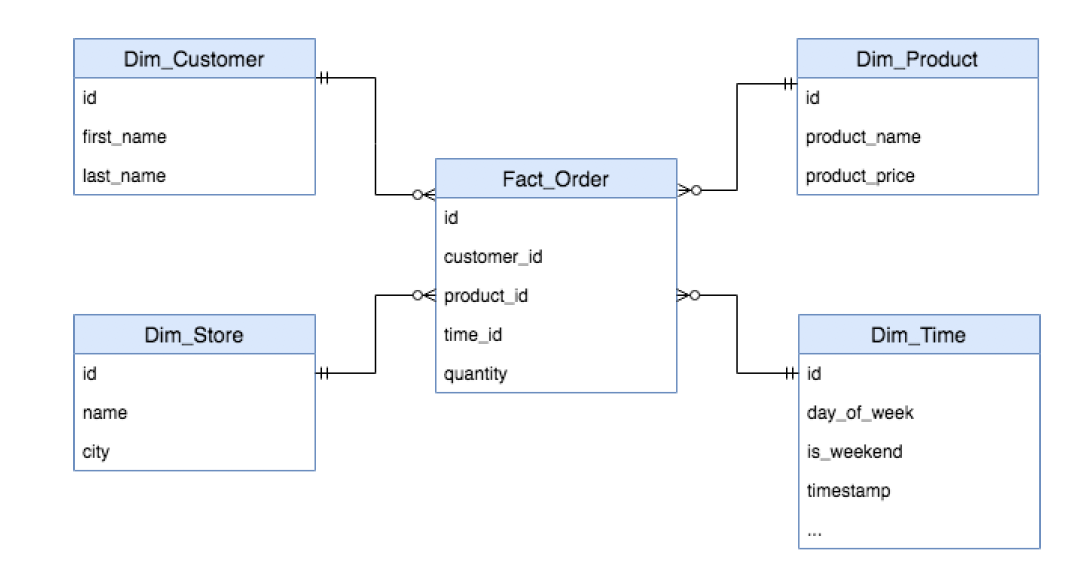
- Dimensions: information on the world (Customer Information)
- Facts: things that happened (Product Orders)
Parallel computing
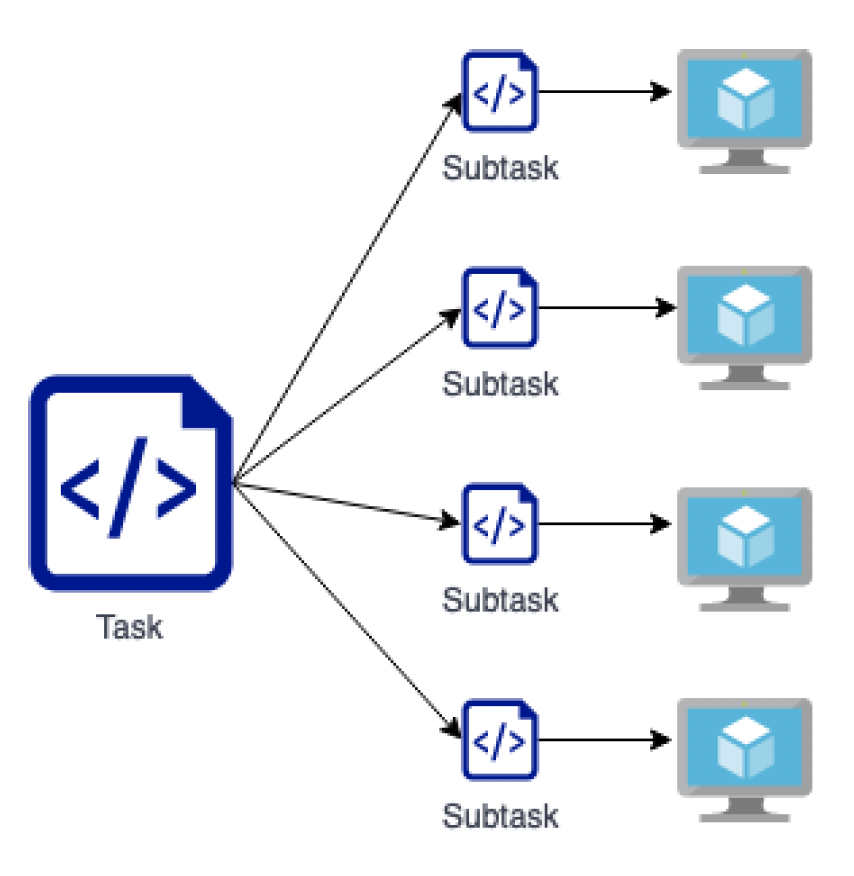
- Memory & Processing power issue
- Split task into subtasks
- Distribute subtasks over sevral computers
Multiprocessing.Pool
from multiprocessing import Pool
def take_mean_age(year_and_group):
year, group = year_and_group
return pd.DataFrame({"Age": group["age"].mean()}, index[year])
# Function to apply a function over multiple cores
@print_timing
def parallel_apply(apply_func, groups, nb_cores):
with Pool(nb_cores) as p:
results = p.map(apply_func, groups)
return pd.concat(results)
# Parallel apply using 1 core
parallel_apply(take_mean_age, athlete_events.groupby('Year'), 1)
# Parallel apply using 2 cores
parallel_apply(take_mean_age, athlete_events.groupby('Year'), 2)
# Parallel apply using 4 cores
parallel_apply(take_mean_age, athlete_events.groupby('Year'), 4)
dask
import dask.dataframe as dd
# Partition dataframe into 4
athlete_events_dask = dd.from_pandas(athlete_events, npartitions = 4)
# Run parallel computations on each partition
result_df = athlete_events_dask.groupby('Year').Age.mean().compute()
Hadoop
MapReduce: Computation
Hive SQL (Initially MapReduce)
HDFS: Storage
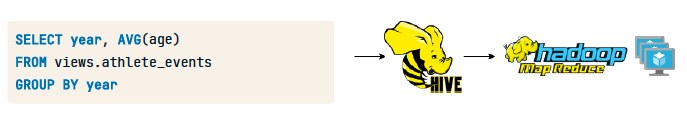
Spark
- Avoid disk writes
- Transformations:
.map().filter() - Actions:
.count().first()
PySpark
>>> # Print the type of athlete_events_spark
>>> print(type(athlete_events_spark))
<class 'pyspark.sql.dataframe.DataFrame'>
>>> # Print the schema of athlete_events_spark
>>> print(athlete_events_spark.printSchema())
root
|-- ID: integer (nullable = true)
|-- Name: string (nullable = true)
|-- Sex: string (nullable = true)
|-- Age: integer (nullable = true)
|-- Height: string (nullable = true)
|-- Weight: string (nullable = true)
|-- Team: string (nullable = true)
|-- NOC: string (nullable = true)
|-- Games: string (nullable = true)
|-- Year: integer (nullable = true)
|-- Season: string (nullable = true)
|-- City: string (nullable = true)
|-- Sport: string (nullable = true)
|-- Event: string (nullable = true)
|-- Medal: string (nullable = true)
>>> # Group by the Year, and find the mean Age
>>> print(athlete_events_spark.groupBy('Year').mean('Age'))
DataFrame[Year: int, avg(Age): double]
>>> # Group by the Year, and find the mean Age
>>> print(athlete_events_spark.groupBy('Year').mean('Age').show())
+----+------------------+
|Year| avg(Age)|
+----+------------------+
|1896|23.580645161290324|
|1924|28.373324544056253|
|2006|25.959151072569604|
|1908|26.970228384991845|
|1952|26.161546085232903|
|1956|25.926673567977915|
|1988|24.079431552931485|
|1994|24.422102596580114|
|1968|24.248045555448314|
|2014|25.987323655694134|
|1904| 26.69814995131451|
|2004|25.639514989213716|
|1932| 32.58207957204948|
|1996|24.915045018878885|
|1998|25.163197335553704|
|1960|25.168848457954294|
|2012| 25.96137770897833|
|1912| 27.53861997940268|
|2016| 26.20791934541204|
|1936|27.530328324986087|
+----+------------------+
only showing top 20 rows
PySpark Submit
#spark-script.py
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
if __name__ == "__main__":
spark = SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()
athlete_events_spark = (spark
.read
.csv("/home/repl/datasets/athlete_events.csv",
header=True,
inferSchema=True,
escape='"'))
athlete_events_spark = (athlete_events_spark
.withColumn("Height",
athlete_events_spark.Height.cast("integer")))
print(athlete_events_spark
.groupBy('Year')
.mean('Height')
.orderBy('Year')
.show())
# A local Spark instance running on 4 threads
$ spark-submit \
--master local[4] \
/home/repl/spark-script.py
+----+------------------+
|Year| avg(Height)|
+----+------------------+
|1896| 172.7391304347826|
|1900|176.63793103448276|
|1904| 175.7887323943662|
|1906|178.20622568093384|
|1908|177.54315789473685|
|1912| 177.4479889042996|
|1920| 175.7522816166884|
|1924|174.96303901437372|
|1928| 175.1620512820513|
|1932|174.22011541632315|
|1936| 175.7239932885906|
|1948|176.17279726261762|
|1952|174.13893967093236|
|1956|173.90096798212957|
|1960|173.14128595600675|
|1964| 173.448573701557|
|1968| 173.9458648072826|
|1972|174.56536284096757|
|1976|174.92052773737794|
|1980|175.52748832195473|
+----+------------------+
only showing top 20 rows
Workflow scheduling frameworks
Dags (Directed Acyclic Graph)
- Set of Nodes
- Directed edges
- No cycles
Tools
- Linux cron
- Spotify Luigi
- Apahce Airflow
Airflow
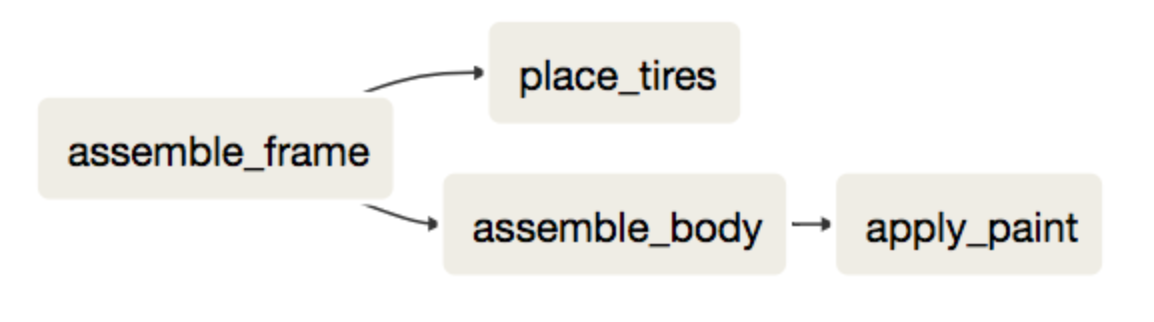
# Create the DAG object
dag = DAG(dag_id="car_factory_simulation",
default_args={"owner": "airflow","start_date": airflow.utils.dates.days_ago(2)},
schedule_interval="0 * * * *")
# Task definitions
assemble_frame = BashOperator(task_id="assemble_frame", bash_command='echo "Assembling frame"', dag=dag)
place_tires = BashOperator(task_id="place_tires", bash_command='echo "Placing tires"', dag=dag)
assemble_body = BashOperator(task_id="assemble_body", bash_command='echo "Assembling body"', dag=dag)
apply_paint = BashOperator(task_id="apply_paint", bash_command='echo "Applying paint"', dag=dag)
# Complete the downstream flow
assemble_frame.set_downstream(place_tires)
assemble_frame.set_downstream(assemble_body)
assemble_body.set_downstream(apply_paint)
# Create the DAG object
dag = DAG(dag_id="example_dag", ..., schedule_interval="0 * * * *")
# Define operations
start_cluster = StartClusterOperator(task_id="start_cluster", dag=dag)
ingest_customer_data = SparkJobOperator(task_id="ingest_customer_data", dag=dag)
ingest_product_data = SparkJobOperator(task_id="ingest_product_data", dag=dag)
enrich_customer_data = PythonOperator(task_id="enrich_customer_data", ..., dag = dag)
# Set up dependency flow
start_cluster.set_downstream(ingest_customer_data)
ingest_customer_data.set_downstream(enrich_customer_data)
ingest_product_data.set_downstream(enrich_customer_data)
Extract, Transform and Load (ETL)
Extract
Data in Database
Application databases
- Transactions
- SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
- OLTP(Online Transaction Processing)
- Focus on Transaction
- Process multiple data source (clients), return the result to clients
- Like transfering money to someone, it cannot stop during the process
- If it failed during the process, rollback, if it succeeded, commit
- Data Integrity
- Real time
- Money transfer, Editing user profile
- Row-oriented
Analytics databases
SELECT
OLAP(Online Analytical Processing)
- Focus on Analytics
- Analaysis on Data Warehouse(DB)
- Based on past data
- Last year revenue
Column-oriented (Redshift)
Extraction from databases
Connection string/URI
postgresql://[user[:password]@][host][:port]
Use in Python
import sqlalchemy
connection_uri = "postgresql://repl:password@localhost:5432/pagila"
db_engine = sqlalchemy.create_engine(connection_uri)
import pandas as pd
pd.read_sql("SELECT * FROM customer", db_engine)
Transform
Pandas
# Get the rental rate column as a string
rental_rate_str = film_df.rental_rate.astype(str)
# Split up and expand the column
rental_rate_expanded = rental_rate_str.str.split(".", expand=True)
# Assign the columns to film_df
film_df = film_df.assign(
rental_rate_dollar=rental_rate_expanded[0],
rental_rate_cents=rental_rate_expanded[1],
)
# Use groupBy and mean to aggregate the column
ratings_per_film_df = rating_df.groupBy('film_id').mean('rating')
# Join the tables using the film_id column
film_df_with_ratings = film_df.join(
ratings_per_film_df,
film_df.film_id==ratings_per_film_df.film_id
)
# Show the 5 first results
print(film_df_with_ratings.show(5))
Pyspark
import pyspark.sql
spark = pyspark.sql.SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()
spark.read.jdbc("jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/pagila", "customer", properties={"user":"repl","password":"password"})
customer_df # PySpark DataFrame with customer data
ratings_df # PySpark DataFrame with ratings data
# Groupby ratings
ratings_per_customer = ratings_df.groupBy("customer_id").mean("rating")
# Join on customer ID
customer_df.join(
ratings_per_customer,
customer_df.customer_id==ratings_per_customer.customer_id
)
Loading
- Analytics
- OLAP
- Aggregate queries
- Column-oriented
- SQL about subset of columns
- Parallelization
- Applications
- OLTP
- Lots of transactions
- Row-oriented
- Stored per record
- Added per transaction
- E.G adding customer is fast (should be)
- MPP Databases (Massively Parallel Processing Databases)
- Amazon Redshift
- Azure SQL data Warehouse
- Google BigQuery
Redshift
First, send data to s3
# Pandas .to_parquet() method
df.to_parquet("./s3://path/to/bucket/customer.parquet")
# PySpark .write.parquet() method
df.write.parquet("./s3://path/to/bucket/customer.parquet")
Second, load s3 data into redshift (standard procedure)
COPY customer
FROM 's3://path/to/bucket/customer.parquet'
FORMAT as parquet
...
pandas.to_sql()
# Transformation on data
recommendations = transform_find_recommendatins(ratings_df)
# Load into PostgreSQL database
recommendations.to_sql("recommendations", db_engine, schema="store", if_exists="replace")
Putting it all together
def extract_table_to_df(tablename, db_engine):
return pd.read_sql("SELECT * FROM {}".format(tablename), db_engine)
def split_columns_transform(df, column, pat, suffixes):
# Converts column into str and splits it on pat...
def load_df_into_dwh(film_df, tablename, schema, db_engine):
return pd.to_sql(tablename, db_engine, schema=schema, if_exists="replace")
db_engines = { ... } # Needs to be configured
def etl():
# Extract
film_df = extract_table_to_df("film", db_engines["store"])
# Transform
film_df = split_columns_transform(film_df, "rental_rate", ".", ["_dollar", "_cents"])
# Load
film_df = load_df_into_dwh(film_df, "film", "store", db_engines["dwh"])
# Define the ETL task using PythonOperator
etl_task = PythonOperator(task_id='etl_film',
python_callable=etl,
dag=dag)
# Set the upstream to wait_for_table and sample run etl()
etl_task.set_upstream(wait_for_table)
etl()
Scheduling with Dags in Airflow
# Define the ETL task using PythonOperator
from airflow.models import DAG
dag = DAG(dag_id="sample",
...,
schedule_interval="0 0 * * *")
# cron
# .------------------------- minute (0 - 59)
# | .----------------------- hour (0 - 23)
# | | .--------------------- day of the month (1 - 31)
# | | | .------------------- month (1 - 12)
# | | | | .----------------- day of the week (0 - 6)
# * * * * * <command>
# Example
0 * * * * # Every hour at the 0th minute
cf. https://crontab.guru
Case Study: Datacamp
Course rating
| user_id | course_id | rating | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 6 | 4 |
| 1 | 1 | 36 | 5 |
| 2 | 1 | 37 | 5 |
| 3 | 1 | 45 | 5 |
# Complete the transformation function
def transform_avg_rating(rating_data):
# Group by course_id and extract average rating per course
avg_rating = rating_data.groupby('course_id').rating.mean()
# Return sorted average ratings per course
sort_rating = avg_rating.sort_values(ascending=False).reset_index()
return sort_rating
# Extract the rating data into a DataFrame
rating_data = extract_rating_data(db_engines)
# Use transform_avg_rating on the extracted data and print results
avg_rating_data = transform_avg_rating(rating_data)
print(avg_rating_data)
| course_id | rating | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 46 | 4.8 |
| 1 | 23 | 4.8 |
| 2 | 96 | 4.69 |
| 3 | 56 | 4.66 |
# Complete the transformation function
def transform_recommendations(avg_course_ratings, courses_to_recommend):
# Merge both DataFrames
merged = courses_to_recommend.merge(avg_course_ratings)
# Sort values by rating and group by user_id
grouped = merged.sort_values("rating", ascending=False).groupby("user_id")
# Produce the top 3 values and sort by user_id
recommendations = grouped.head(3).sort_values("user_id").reset_index()
final_recommendations = recommendations[["user_id", "course_id","rating"]]
# Return final recommendations
return final_recommendations
# Use the function with the predefined DataFrame objects
recommendations = transform_recommendations(avg_course_ratings, courses_to_recommend)
Scheduling
connection_uri = "postgresql://repl:password@localhost:5432/dwh"
db_engine = sqlalchemy.create_engine(connection_uri)
def load_to_dwh(recommendations):
recommendations.to_sql("recommendations", db_engine, if_exists="replace")
# Define the DAG so it runs on a daily basis
dag = DAG(dag_id="recommendations",
schedule_interval="0 0 * * *")
# Make sure `etl()` is called in the operator. Pass the correct kwargs.
task_recommendations = PythonOperator(
task_id="recommendations_task",
python_callable=etl,
op_kwargs={"db_engines": db_engines},
)
