Streamlined Data Ingestion with pandas
Streamlined Data Ingestion with Pandas
Introduction to Flat files
Flat files
- Data stored as plain text (no format)
- One row per line
- values seperated by a delimiter
Modifying flat file imports
col_names = ['STATEFIPS', 'STATE', 'zipcode', 'agi_stub', 'N1']
col_nums = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
# Choose columns to load by name
tax_data_v1 = pd.read_csv('us_tax_data_2016.csv', usecols=col_names)
# Choose columns to load by number
tax_data_v2 = pd.read_csv('us_tax_data_2016.csv',
usecols=col_nums)
print(tax_data_v1.equals(tax_data_v2))
True
tax_data_next500 = pd.read_csv('us_tax_data_2016.csv', nrows=500, skiprows=1000, header=None)
- nrows: choose N number of rows
- skiprows: skip first N rows
# tax_data_first1000 is dataframe
# extracting column name with list
col_names = list(tax_data_first1000)
tax_data_next500 = pd.read_csv('us_tax_data_2016.csv', nrows=500, skiprows=1000,header=None,names=col_names) print(tax_data_next500.head(1))
Handling errors and missing data
Specifying Data Types
tax_data = pd.read_csv("us_tax_data_2016.csv", dtype={"zipcode": str})
Customizing Missing Data Values
tax_data = pd.read_csv("us_tax_data_2016.csv", na_values={"zipcode":0})
print(tax_data[tax_data.zipcode.isna()])
Lines with Errors
>>> tax_data = pd.read_csv("us_tax_data_2016_corrupt.csv", error_bad_lines=False, warn_bad_lines=True)
b'Skipping line 3: expected 147 fields, saw 148\n'
Introduction to spreadsheets
Loading Select Columns and Rows
# Read columns W-AB and AR of file, skipping metadata header
survey_data = pd.read_excel("fcc_survey_with_headers.xlsx", skiprows=2, usecols="W:AB, AR")
# View data
print(survey_data.head())
Selecting Sheets to Load
Loading Select Sheets
# Get the second sheet by position index
survey_data_sheet2 = pd.read_excel('fcc_survey.xlsx', sheet_name=1)
# Get the second sheet by name
survey_data_2017 = pd.read_excel('fcc_survey.xlsx', sheet_name='2017')
>>> print(survey_data_sheet2.equals(survey_data_2017))
True
- Passing
sheet_name=Nonereads all sheet in a workbook
>>> survey_responses = pd.read_excel("fcc_survey.xlsx", sheet_name=None)
>>> print(type(survey_responses))
<class 'collections.OrderedDict'>
# key would be 2016, 2017 here
>> for key, value in survey_responses.items():
>> print(key, type(value))
2016 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
2017 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Modifying imports true/false data
# Load data, casting True/False columns as Boolean
bool_data = pd.read_excel("fcc_survey_booleans.xlsx",
dtype={
"AttendedBootcamp": bool,
"AttendedBootCampYesNo": bool,
"AttendedBootcampTF":bool,
"BootcampLoan": bool,
"LoanYesNo": bool,
"LoanTF": bool},
true_values=["Yes"], false_values=["No"])
Modifying imports: parsing dates
Parsing Dates
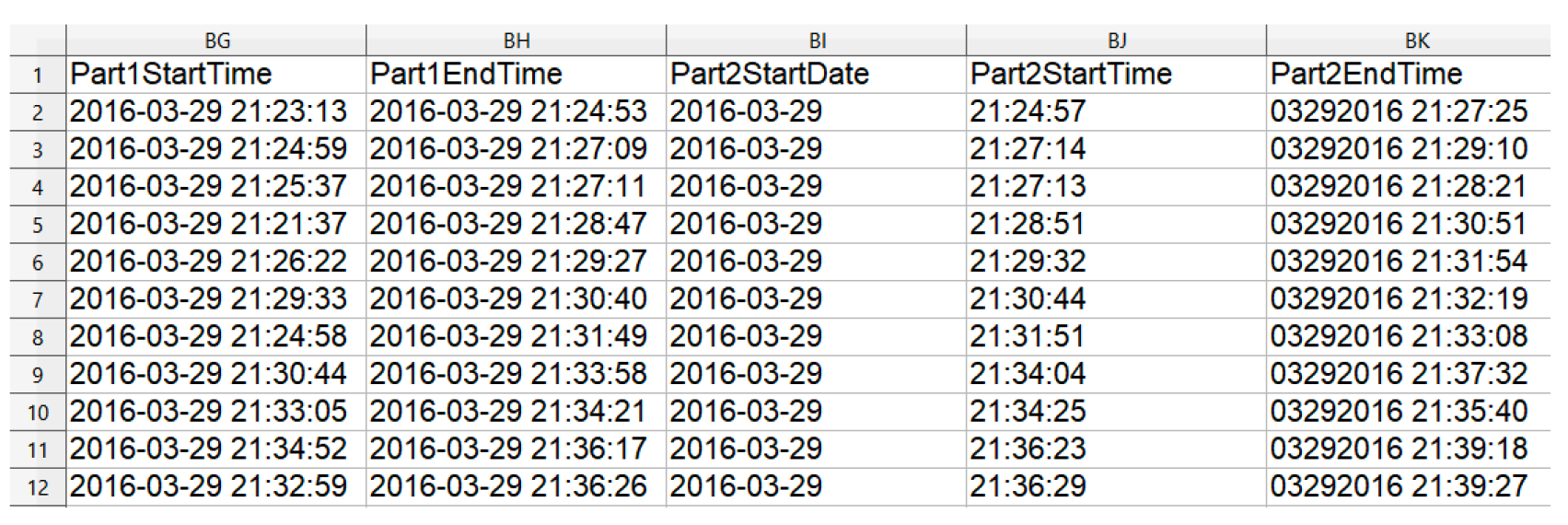
# List columns of dates to parse
date_cols = ["Part1StartTime", "Part1EndTime"]
# Load file, parsing standard datetime columns
survey_df = pd.read_excel("fcc_survey.xlsx", parse_dates=date_cols)
# List columns of dates to parse
date_cols = ["Part1StartTime","Part1EndTime", [["Part2StartDate","Part2StartTime"]]]
# Load file, parsing standard and split datetime columns
survey_df = pd.read_excel("fcc_survey.xlsx", parse_dates=date_cols)
print(survey_df.head(3))
| Part2StartDate_Part2StartTime | Age | ,,, | SchoolMajor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2016-03-29 21:24:57 | 28.0 | Nan | |
| 1 | 2016-03-29 21:27:14 | 22.0 | Nan | |
| 2 | 2016-03-29 21:27:13 | 19.0 | Nan |
[3 rows x 98 columns]
# List columns of dates to parse
date_cols = {"Part1Start":"Part1StartTime",
"Part1End":"Part1EndTime","Part2Start": ["Part2StartDate","Part2StartTime"]}
# Load file, parsing standard and split datetime columns
survey_df = pd.read_excel("fcc_survey.xlsx", parse_dates=date_cols)
print(survey_df.Part2Start.head(3))
0 2016-03-29 21:24:57
1 2016-03-29 21:27:14
2 2016-03-29 21:27:13
Name: Part2Start, dtype: datetime64[ns]
Datetime Formatting
| Code | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| %Y | Year (4-digit) | 1999 |
| %m | Month (zero-padded) | 03 |
| %d | Day (zero-padded) | 01 |
| %H | Hour (24-hour clock) | 21 |
| %M | Minute (zero-padded) | 09 |
| %S | Second (zero-padded) | 05 |
format_string = "%m%d%Y %H:%M:%S"
survey_df["Part2EndTime"] = pd.to_datetime(survey_df["Part2EndTime"], format=format_string)
print(survey_df.Part2EndTime.head())
0 2016-03-29 21:27:25
1 2016-03-29 21:29:10
2 2016-03-29 21:28:21
3 2016-03-29 21:30:51
4 2016-03-29 21:31:54
Name: Part2EndTime, dtype: datetime64[ns]
Introduction to databases
Pass
Importing JSON Data and Working with APIs
Introduction to JSON
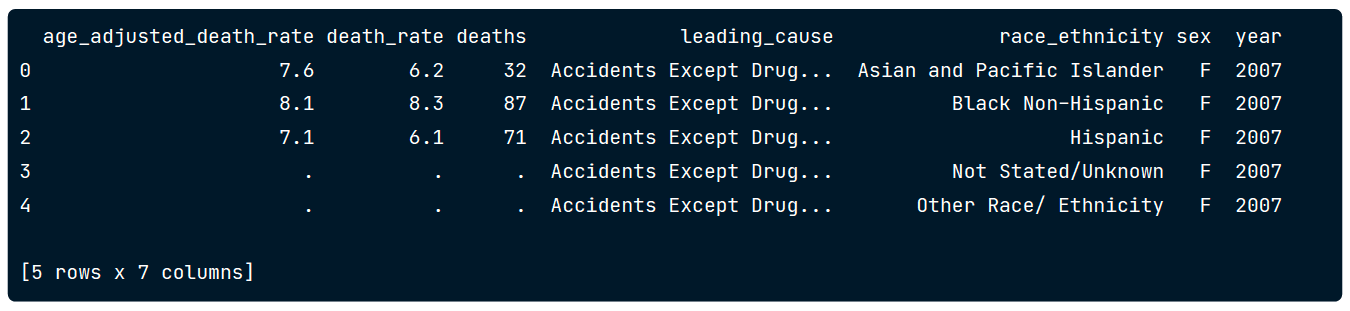
Record Orientation
[ { "age_adjusted_death_rate": "7.6", "death_rate": "6.2", "deaths": "32", "leading_cause": "Accidents Except Drug Posioning (V01-X39, X43, X45-X59, Y85-Y86)", "race_ethnicity": "Asian and Pacific Islander", "sex": "F", "year": "2007" }, { "age_adjusted_death_rate": "8.1", "death_rate": "8.3", "deaths": "87", ...Column Orientation
{ "age_adjusted_death_rate": { "0": "7.6", "1": "8.1", "2": "7.1", "3": ".", "4": ".", "5": "7.3", "6": "13", "7": "20.6", "8": "17.4", "9": ".", "10": ".", "11": "19.8", ...Split oriented
{ "columns": ["age_adjusted_death_rate", "death_rate", "deaths", "leading_cause", "race_ethnicity", "sex", "year"], "index": [...], "data": [ [ "7.6",
Specifying Orientation
import pandas as pd
death_causes = pd.read_json("nyc_death_causes.json", orient="split")
print(death_causes.head())
Introduction to APIs
Making Requests
import requests
import pandas as pd
api_url = "https://api.yelp.com/v3/businesses/search"
# Set up parameter dictionary according to documentation
params = {"term": "bookstore", "location": "San Francisco"}
# Set up header dictionary w/ API key according to documentation
headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer {}".format(api_key)}
# Call the API
response = requests.get(api_url, params=params, headers=headers)
# Extract JSON data from the response
data = response.json()
# Load data to a data frame
cafes = pd.DataFrame(data['businesses'])
Working with nested JSONs

Loading Nested JSON Data
import pandas as pd
import requests
from pandas.io.json import json_normalize
# Set up headers, parameters, and API endpoint
api_url = "https://api.yelp.com/v3/businesses/search"
headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer {}".format(api_key)}
params = {"term": "bookstore", "location": "San Francisco"}
# Make the API call and extract the JSON data
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=headers, params=params)
data = response.json()
# Flatten data and load to data frame, with _ separators
bookstores = json_normalize(data["businesses"], sep="_")
>>> print(list(bookstores))
['alias', 'categories', 'coordinates_latitude', 'coordinates_longitude', ... 'location_address1', 'location_address2', 'location_address3', 'location_city', 'location_country', 'location_display_address', 'location_state', 'location_zip_code', ... 'url']
Deeply Nested Data
>>> print(bookstores.categories.head())
0 [{'alias': 'bookstores', 'title': 'Bookstores'}]
1 [{'alias': 'bookstores', 'title': 'Bookstores'...
2 [{'alias': 'bookstores', 'title': 'Bookstores'}]
3 [{'alias': 'bookstores', 'title': 'Bookstores'}]
4 [{'alias': 'bookstores', 'title': 'Bookstores'...
Name: categories, dtype: object
# Flatten categories data, bring in business details
df = json_normalize(data["businesses"],
sep="_",
record_path="categories", # for nested data
meta=["name", "alias", "rating", ["coordinates","latitude"],
["coordinates","longitude"]
], # list of attributes/columns
meta_prefix="biz_" # prefix to meta column names
)
Combining multiple datasets
# Put bookstore datasets together, renumber rows
bookstores = first_20_bookstores.append(next_20_bookstores, ignore_index=True)
